Are you concerned about your hair dryer’s electricity consumption? Many people wonder whether using hot or cold settings affects their energy bills. Understanding electrical draw differences helps you make informed decisions about energy efficiency and operational costs.
Hot settings consume 1,200-1,875 watts, while cold settings use only 70-140 watts – representing a 1,300% increase in power usage. This dramatic difference occurs because cold settings only power the motor and fan, while hot settings activate energy-intensive heating elements.
Let’s explore the technical details and practical implications of these power consumption differences.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow Much Power Does a Hair Dryer Use on Hot Settings?
Understanding power consumption on hot settings helps you calculate operational costs and energy efficiency for your business or personal use.
Hair dryers typically consume 1,500-2,000 watts on hot settings, with professional-grade models reaching up to 2,500 watts. Standard household models operate around 1,500 watts on high heat, while some high-end models can consume as much as 3,000 watts.
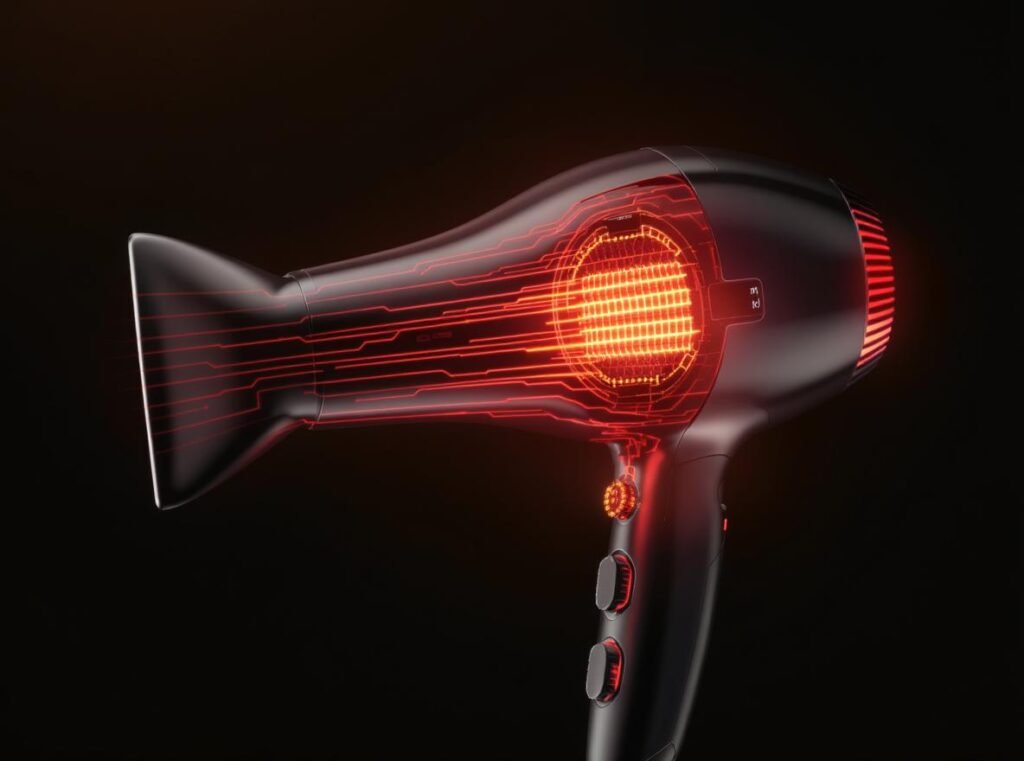
The heating element accounts for approximately 90% of total power consumption when operating on hot settings. This nichrome wire coil converts electrical energy into heat energy, which explains the dramatic power requirements.
Modern hair dryers like the Conason P1C are designed with multiple heat settings to optimize power usage. Here’s how power consumption breaks down:
| Setting Type | Power Range (Watts) | Heating Element Usage | Motor Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Heat | 1,500-2,000 | 1,200-1,600 watts | 300-400 watts |
| Medium Heat | 1,000-1,500 | 700-1,200 watts | 300-400 watts |
| Low Heat | 800-1,200 | 500-900 watts | 300-400 watts |
Professional-grade hair dryers often feature advanced heating technology that maintains consistent temperatures while optimizing power consumption. This efficiency becomes crucial for salons and businesses that use hair dryers continuously throughout the day.
The heating elements in quality hair dryers use ceramic or tourmaline technology, which distributes heat more evenly while potentially reducing overall power consumption compared to traditional metal heating elements.
How Much Electricity Does Cold Setting Consume?
Cold settings offer significant energy savings, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious users and businesses looking to reduce operational costs.
Cold or cool air settings consume dramatically less electricity, using only 70-140 watts. Some models can operate on as little as 66 watts in unheated air mode, representing the power needed to run just the motor and fan without any heating elements active.
The power consumption on cold settings depends on several factors:
Motor Efficiency and Type
- High-quality motors consume less power while maintaining strong airflow
- Brushless motors typically offer better energy efficiency
- AC motors provide consistent power at high speeds
Fan Speed Variations
- Higher speeds require more power even without heat
- Low air settings can use as little as 66 watts
- High air settings without heat typically consume 140-200 watts
Cold air drying offers several advantages beyond energy savings:
- Reduces heat damage to hair by closing hair cuticles
- Helps set hairstyles for longer-lasting results
- Extends the lifespan of hair dryer components
- Suitable for heat-sensitive hair types
- Creates less stress on electrical circuits
For wholesale buyers and retailers, promoting the energy efficiency of cold settings can be a valuable selling point for environmentally conscious consumers seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.
Why Do Hot Settings Use More Electricity?
The dramatic difference in power consumption between hot and cold settings stems from the additional components required to generate and maintain heat.
Hot settings require electricity to power both the motor and heating elements simultaneously. The heating element is essentially a high-resistance wire that converts electrical energy into heat energy, accounting for approximately 90% of total power consumption.
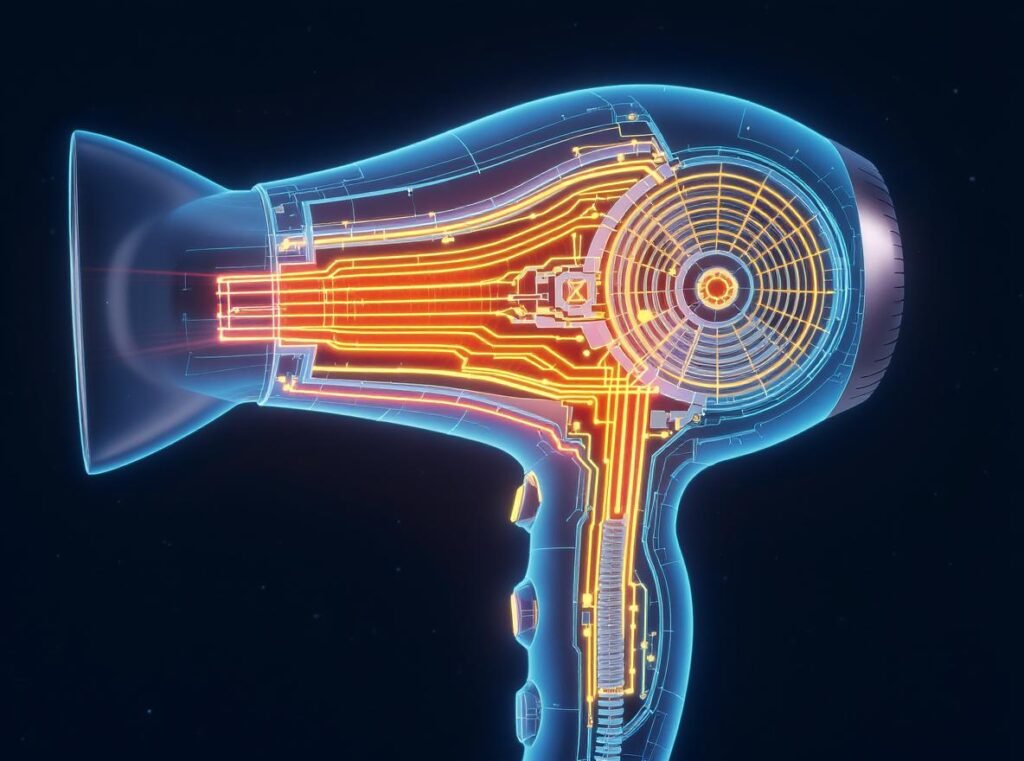
The heating process involves several power-intensive components:
Primary Heating Element
The nichrome wire coil requires 1,000-1,600 watts to reach and maintain desired temperatures. This process is inherently energy-intensive, requiring substantial power to generate the heat necessary for effective hair drying.
Temperature Control Systems
Modern hair dryers include sophisticated temperature control systems that continuously monitor and adjust heat output. These systems require additional power to operate sensors and control circuits that maintain consistent temperatures.
Safety Feature Power Requirements
Hot settings activate various safety features including:
- Overheat protection circuits that prevent damage
- Temperature sensors for automatic regulation
- Automatic shut-off mechanisms for safety
- Thermal fuses that protect against overheating
These safety components, while essential for user protection, contribute to overall power consumption during hot air operation.
Does Wattage Affect Drying Performance?
Understanding the relationship between wattage and performance helps you choose the right hair dryer for specific needs and applications.
Higher wattage generally translates to better drying performance through faster drying times, stronger airflow, and higher heat output. However, wattage alone doesn’t determine performance – motor efficiency, airflow design, and heating element quality all play crucial roles.

The relationship between wattage and performance includes several key factors:
Drying Speed Benefits
- More power means more heat and airflow generation
- Higher wattage motors can generate stronger air movement
- Increased electrical energy converts to more thermal energy
- Professional results require adequate power for thick or long hair
Performance Optimization Features
- Engineered air intake systems maximize airflow volume
- Aerodynamic design reduces turbulence and increases efficiency
- Concentrated nozzles focus airflow for targeted drying
- Advanced motor technology provides consistent power delivery
Technology Advancements
- Ceramic heating elements provide even heat distribution
- Tourmaline technology reduces overall drying time
- Ionic technology breaks down water molecules more efficiently
- Brushless motors increase efficiency and component longevity
The Conason P1C demonstrates how advanced engineering can deliver professional performance while maintaining energy efficiency across all settings, making it ideal for both salon use and retail applications.
Are There Energy-Efficient Hair Dryer Options?
Energy efficiency has become increasingly important for both consumers and businesses seeking to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
Modern energy-efficient hair dryers incorporate brushless motors, advanced heating elements, and smart temperature control to reduce power consumption by 25-33% compared to traditional models while maintaining comparable performance.

Several manufacturers now offer energy-efficient options:
| Model/Brand | Power Consumption | Energy Savings | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valera ePower | 1,600 watts | 25-33% savings | Advanced motor technology |
| BarBar ECO-8000 | 1,000 watts | 45% reduction | Optimized airflow design |
| Professional Models | 1,200-1,600 watts | 20-30% savings | Brushless motors |
Advanced Energy-Saving Features
- Brushless DC motors offer superior efficiency with reduced friction
- Variable speed controls optimize power usage for different hair types
- Precise temperature control prevents energy waste from overheating
- Rapid heating reduces warm-up time and energy consumption
Smart Technology Integration
- Automatic shut-off prevents unnecessary energy use
- Intelligent heat sensors maintain optimal temperatures
- Consistent heat output minimizes energy fluctuations
- Lightweight construction requires less power for operation
For businesses in the hair care industry, investing in energy-efficient models can significantly reduce operational costs over time while appealing to environmentally conscious consumers and meeting sustainability goals.
How to Calculate Your Hair Dryer’s Energy Costs?
Understanding energy costs helps both consumers and businesses make informed decisions about hair dryer usage and selection.
To calculate energy costs, use this formula: Daily Cost = (Wattage × Hours Used ÷ 1,000) × Electricity Rate per kWh. For example, a 1,500-watt dryer used for 10 minutes daily costs approximately $11-14 annually at typical electricity rates.

Here’s a comprehensive cost breakdown:
| Usage Scenario | Daily kWh | Monthly kWh | Annual Cost ($0.12/kWh) | Annual Cost ($0.15/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Home Use – 10 min daily (1,500W) | 0.25 | 7.5 | $10.95 | $13.69 |
| Home Use – 15 min daily (1,500W) | 0.375 | 11.25 | $16.43 | $20.53 |
| Professional Use – 10 min daily (2,000W) | 0.33 | 9.9 | $14.45 | $18.07 |
| Salon Use – 4 hours daily (1,500W) | 6.0 | 180 | $262.80 | $328.50 |
Business Cost Considerations
- Professional salons using hair dryers 4+ hours daily can spend $260-330 annually per dryer
- Energy-efficient models can reduce these costs by 25-33%
- Multiple dryer operations significantly impact monthly utility bills
- Peak usage hours may affect electricity rates in commercial settings
Cost-Saving Strategies
- Use appropriate heat levels for different hair types
- Implement staff training on efficient usage patterns
- Consider energy-efficient models for long-term savings
- Monitor usage patterns to optimize operational costs
Professional establishments can achieve significant savings by selecting efficient equipment and training staff on optimal usage techniques.
What Factors Affect Hair Dryer Power Consumption?
Multiple factors influence how much electricity your hair dryer consumes, affecting both performance and operational costs.
Power consumption varies based on heat settings, fan speed, motor efficiency, environmental conditions, and usage patterns. The heat setting remains the primary factor, with hot settings using 10-15 times more power than cold settings.

Technical Factors
- Heat settings represent the most significant variable in power consumption
- Airflow speed increases motor power consumption, though modestly compared to heating elements
- Motor efficiency affects overall energy usage and performance
- Heating element quality impacts both power draw and heat distribution
Environmental Influences
- Ambient temperature affects heating element efficiency requirements
- Humidity levels impact required drying time and power usage
- Altitude can affect motor performance and airflow generation
- Voltage fluctuations influence actual power draw from rated specifications
Usage Pattern Variables
- Hair type and length determine required drying time
- Frequent use of high heat settings increases energy consumption
- Alternating between settings can optimize energy usage
- Proper technique reduces overall drying time requirements
Maintenance Impact
- Clogged filters reduce efficiency and increase power consumption
- Dirty heating elements require more energy to reach target temperatures
- Regular cleaning maintains optimal airflow and heat distribution
- Component wear affects overall efficiency over time
Understanding these factors helps optimize hair dryer selection and usage for maximum efficiency while maintaining desired performance levels.
Summary
Hot settings consume 1,200-1,875 watts compared to cold settings using only 70-140 watts, representing a 1,300% increase in power consumption. This dramatic difference occurs because heating elements account for 90% of power usage, making setting selection crucial for energy efficiency.
Ready to explore energy-efficient hair dryer options for your business? Browse our complete collection of professional-grade hair dryers, including the innovative Conason P1C with advanced energy-saving features and optimized performance. Contact us today for wholesale pricing and discover how our high-efficiency models can reduce your operational costs by up to 30% while delivering superior professional results.



