Planning to expand your hair dryer business globally? Understanding voltage differences is crucial for success. Many distributors struggle with compatibility issues that can damage both products and customer relationships across different electrical systems.
The main manufacturing differences between 110V and 220V hair dryers involve motor specifications, heating element configurations, circuit board designs, and safety compliance requirements. 110V models require motors designed for 15-20 amp current draw with complex switching circuits, while 220V units operate efficiently at 8-10 amps with simpler designs but enhanced insulation for higher voltage operation.
Ready to discover how these technical differences impact your global sourcing strategy? Let’s explore the manufacturing variations that determine international market success.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow Do Motor Specifications Differ Between 110V and 220V Hair Dryers?
Motor design represents the most critical manufacturing difference between voltage systems. Understanding these specifications helps distributors select appropriate products for target markets and avoid performance issues.
110V hair dryers require AC universal motors designed for 15-20 amperes of current draw, while 220V systems operate efficiently with just 8-10 amperes for equivalent power output. Both systems achieve similar speeds of 35,000 rpm no-load and 13,000-15,000 rpm under load, but the winding configurations differ significantly.
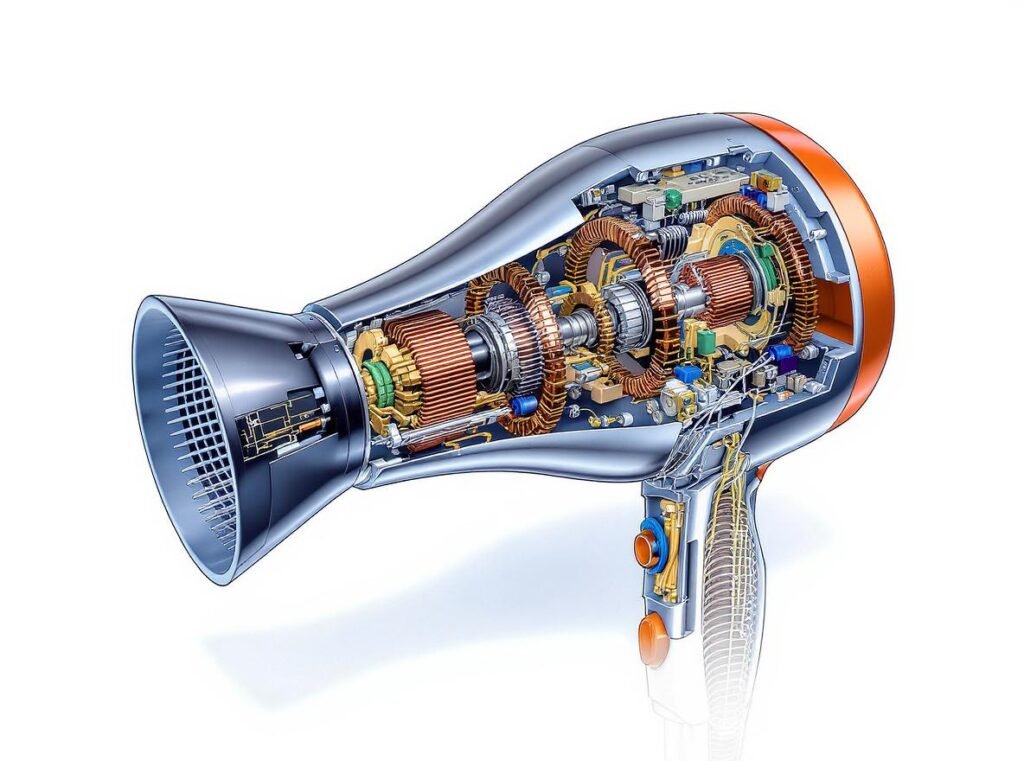

The fundamental electrical relationship (Power = Voltage × Current) explains why 220V systems achieve the same power with half the current. This leads to improved efficiency and reduced heat generation in 220V models.
Motor winding configurations vary dramatically between voltage systems:
110V Motor Characteristics:
- Higher turn counts with finer wire to handle lower voltage
- Enhanced cooling systems to manage higher current flow
- Thicker copper conductors in windings
- More complex thermal management requirements
220V Motor Characteristics:
- Fewer turns with thicker wire for higher voltage operation
- Simpler cooling requirements due to lower current
- Enhanced insulation materials for voltage protection
- More efficient power transfer characteristics
| Motor Specification | 110V Models | 220V Models |
|---|---|---|
| Current Draw | 15-20 amps | 8-10 amps |
| Winding Configuration | High turns, fine wire | Low turns, thick wire |
| Cooling Requirements | Enhanced systems | Standard systems |
| Thermal Management | Complex | Simplified |
Manufacturing costs for 110V motors typically run 15-20% higher due to increased copper requirements and enhanced cooling systems needed to manage the higher current flow.
What Are the Key Heating Element Design Differences?
Heating element configuration represents another critical manufacturing difference that directly impacts drying performance and energy efficiency. These components must be optimized for their specific voltage systems.
110V hair dryers use nichrome wire configured with higher resistance coils to generate adequate heat at lower voltage, typically producing 1000-1875 watts. 220V systems utilize lower resistance coils optimized for higher voltage operation, producing 1600-2200 watts more efficiently.
The heating element design philosophy differs fundamentally between voltage systems:
110V Heating Elements:
- Higher resistance coils (typically 6-8 ohms) for adequate heat generation
- Series/parallel switching mechanisms for multiple heat settings
- Diode control systems for temperature regulation
- More complex switching circuits to manage power delivery
220V Heating Elements:
- Lower resistance coils (12-16 ohms) optimized for higher voltage
- Simpler switching mechanisms due to more effective power transfer
- Direct AC connections without complex voltage reduction
- Enhanced insulation materials for high-voltage operation
The manufacturing approach reflects these different requirements:
- 110V elements require more sophisticated engineering to achieve target heat output
- 220V elements benefit from simpler designs with fewer components
- Both systems achieve similar temperature outputs but through different electrical pathways
- Safety considerations vary significantly between voltage levels
Manufacturing costs for heating elements typically favor 110V systems in component complexity, while 220V systems require more expensive high-voltage rated materials and enhanced insulation.
How Do Internal Circuit Boards Vary Between Voltage Systems?
Circuit board design varies significantly between 110V and 220V hair dryers, affecting component selection, layout complexity, and manufacturing costs. These differences directly impact product reliability and performance.
110V hair dryers typically incorporate diode control systems for speed regulation, using half-wave rectification to provide low-speed operation by cutting the AC waveform in half. 220V systems benefit from simpler circuit board designs with direct AC connections and less complex speed control systems.

The circuit board complexity reflects the different electrical challenges:
110V Circuit Board Features:
- Diode control systems for speed regulation
- Half-wave rectification circuits for low-speed operation
- Complex voltage switching mechanisms
- Components rated for high current (15-20 amps)
- Enhanced heat dissipation designs
220V Circuit Board Features:
- Simpler direct AC connection systems
- Fewer components for speed control
- Higher voltage-rated components (275-300V)
- Enhanced insulation between circuit traces
- Specialized surge protection circuits
| Circuit Feature | 110V Design | 220V Design |
|---|---|---|
| Speed Control | Diode systems | Direct AC |
| Component Rating | 125-150V/15-20A | 275-300V/8-10A |
| Circuit Complexity | High | Moderate |
| Heat Management | Enhanced | Standard |
The cost implications vary by approach. 110V systems require more components and complex switching circuits, while 220V systems need higher-rated components with enhanced insulation. Manufacturing costs typically favor 220V designs due to their simpler architecture, though component costs may be higher.
What Safety Features Are Required for Each Voltage Type?
Safety requirements represent one of the most significant manufacturing differentiators between voltage systems. Understanding these requirements helps distributors navigate compliance costs and certification complexities.
110V hair dryers destined for North American markets must comply with UL 859 (household) or UL 1727 (commercial) standards, mandating integral GFCI or IDCI protection. 220V systems follow IEC 60335-2-23 standards for CE certification, emphasizing thermal protection and electromagnetic compatibility.

The safety approaches reflect different regulatory philosophies:
110V Safety Requirements (UL Standards):
- Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) protection built into the plug
- Immersion Detection Circuit Interrupter (IDCI) capabilities
- Thermal cutoffs rated for high current interruption (AC125V/15A)
- Double insulation on motor windings
- Enhanced cord strain relief for higher current handling
220V Safety Requirements (IEC Standards):
- Class II double insulation throughout the device
- Thermal protection with bimetallic strips (AC230V/10A)
- Enhanced creepage and clearance distances
- Surge arrestors for voltage spike protection
- Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) compliance
The testing requirements differ significantly:
- 110V models undergo water immersion testing and GFCI functionality verification
- 220V models require high-voltage breakdown testing at 2,500V or higher
- Both systems need thermal protection testing, but at different electrical ratings
- Certification costs typically run 25-40% higher for 220V models
Manufacturing costs for safety components reflect these different approaches, with 110V models requiring more complex integrated safety circuits and 220V models needing higher-rated components throughout the electrical system.
How Do Power Cord and Plug Specifications Differ?
Power cord and plug design represents a visible manufacturing difference that affects both safety and market compliance. These components must accommodate different current loads while meeting regional electrical standards.
110V systems use NEMA 1-15 or NEMA 5-15 plugs with 14-16 AWG wire rated for 120V operation, while 220V systems utilize various plug types including Type C, E, F, and G configurations with 10-12 AWG wire rated for 230V operation.

The engineering requirements differ significantly:
110V Power Cord Design:
- Thicker conductors (14-16 AWG) to handle 15-20 amp current safely
- Enhanced strain relief at both cord ends
- GFCI integration in many North American models
- Standardized NEMA plug configurations
220V Power Cord Design:
- Thinner conductors (10-12 AWG) adequate for 8-10 amp operation
- Higher voltage insulation throughout the cord length
- Multiple plug configurations for different international markets
- Enhanced jacket materials to prevent voltage breakdown
| Cord Specification | 110V Models | 220V Models |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Gauge | 14-16 AWG | 10-12 AWG |
| Insulation Rating | 300V | 450V |
| Current Capacity | 15-20 amps | 8-10 amps |
| Plug Varieties | 2-3 types | 8-12 types |
The physical size difference is notable, with 110V power cords typically 20-30% larger than 220V equivalents due to thicker conductors. However, 220V cords require more sophisticated insulation materials and multiple plug variants for different markets.
Manufacturing costs vary by 15-30%, with 220V models typically more expensive due to enhanced insulation requirements and the need to stock multiple plug configurations for different international markets.
What Are the Dual-Voltage Manufacturing Considerations?
Dual-voltage hair dryers represent a manufacturing compromise attempting to address multiple markets with a single product design. However, this approach involves significant engineering challenges and cost implications.
Dual-voltage systems require either voltage switching mechanisms or auto-sensing transformers to accommodate both 110V and 220V operation. This complexity adds manufacturing cost and potential failure points, with performance often compromised compared to single-voltage optimized designs.
The technical approaches vary among manufacturers:
Auto-Sensing Systems:
- Voltage detection circuits that automatically configure internal components
- Automatic switching relays for seamless operation
- Dual-rated heating elements and motors
- Enhanced safety monitoring systems
Manual Switching Systems:
- Physical switches that reconfigure electrical circuits
- User-operated voltage selection mechanisms
- Dual heating element configurations
- Warning systems to prevent incorrect operation
The manufacturing complexity affects multiple aspects:
- Component costs increase 40-60% due to dual-rated requirements
- Motors must accommodate both voltage ranges, often compromising performance
- Testing procedures become more complex, requiring validation at both voltages
- Certification costs double as products must meet multiple international standards
| System Type | Cost Premium | Performance Impact | Complexity Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto-Sensing | 50-60% | Minimal | High |
| Manual Switch | 40-50% | Moderate | Medium |
| Single Voltage | Baseline | Optimal | Low |
Despite these challenges, dual-voltage models can be attractive for distributors serving multiple markets, as they reduce inventory complexity and provide flexibility for end users. However, premium manufacturers often avoid dual-voltage designs due to performance compromises.
How Do Manufacturing Costs Compare Between Voltage Types?
Understanding cost implications helps distributors make informed sourcing decisions. Manufacturing costs vary significantly based on voltage requirements, component complexity, and certification needs.
110V hair dryers typically cost 15-25% more to manufacture than 220V models due to higher current requirements and complex switching circuits, while dual-voltage models increase costs by 40-60% compared to single-voltage designs.

The cost breakdown reveals several key factors:
110V Cost Drivers:
- Higher-capacity motors with enhanced cooling systems
- Complex diode control circuits for speed regulation
- Thicker power cords with larger conductors
- GFCI/IDCI safety integration
- Current-rated components throughout
220V Cost Drivers:
- Higher voltage-rated components (275-300V)
- Enhanced insulation materials throughout
- Multiple plug configurations for different markets
- More extensive safety testing requirements
- CE certification and compliance costs
| Cost Component | 110V Premium | 220V Premium | Dual-Voltage Premium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor System | $8-12 | $6-10 | $15-20 |
| Heating Elements | $3-5 | $2-4 | $6-8 |
| Circuit Boards | $4-6 | $3-5 | $8-12 |
| Safety Components | $2-4 | $3-6 | $5-8 |
| Testing/Certification | $1-2 | $2-4 | $4-8 |
| Total Impact | 15-25% | 12-20% | 40-60% |
Production volume significantly affects these calculations. High-volume manufacturing can reduce per-unit premiums, while specialty or low-volume models may see even higher cost differences.
For distributors, understanding these cost structures helps in pricing strategy development, market selection decisions, and customer value proposition development.
Which Voltage Configuration Should Global Distributors Choose?
Selecting the optimal voltage configuration requires balancing market coverage, inventory complexity, and cost considerations. The decision impacts operational efficiency and competitive positioning.
Global distributors should prioritize 220V models for international markets due to broader compatibility, representing 70-75% of global markets, while maintaining 110V inventory for North American markets and considering dual-voltage options only for premium travel segments.

Market distribution analysis reveals clear patterns:
220V Market Coverage (70-75% of global markets):
- European Union countries
- Most of Asia-Pacific region
- Africa and Middle East
- South America (with some exceptions)
- Australia and New Zealand
110V Market Coverage (25-30% of global markets):
- United States and Canada
- Parts of Central America
- Japan and some Asian markets
- Limited South American countries
The strategic implications suggest different approaches:
220V-First Strategy Benefits:
- Addresses the largest market segment globally
- Simpler inventory management for international distribution
- Lower manufacturing costs for most markets
- Reduced certification complexity
110V Specialization Benefits:
- Targets high-value North American consumers
- Premium market positioning opportunities
- Higher margins justify additional complexity
- Specialized market expertise advantage
Dual-Voltage Considerations:
- Suitable for premium travel segments
- Reduces inventory complexity for mixed markets
- Higher costs limit mass market viability
- Performance compromises may affect customer satisfaction
| Strategy | Market Coverage | Inventory Complexity | Cost Efficiency | Recommended For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 220V Primary | 70-75% | Low | High | Global distributors |
| 110V Focus | 25-30% | Low | Medium | North American specialists |
| Dual-Voltage | 100% | Medium | Low | Premium travel market |
For most global distributors, a 220V-primary strategy with selective 110V capabilities provides the best balance of market coverage and operational efficiency.
What Are the Key Certification and Compliance Differences?
Certification requirements vary significantly between voltage systems, affecting time-to-market, costs, and regulatory compliance strategies. Understanding these differences helps distributors plan product launches and budget appropriately.
110V hair dryers require UL certification for North American markets, focusing on electrical safety and GFCI functionality, while 220V models need CE marking for European markets and various other certifications for Asian and other international markets.

The certification landscape reflects different regulatory approaches:
110V Certification Requirements:
- UL 859 (household) or UL 1727 (commercial) testing
- GFCI/IDCI functionality verification
- Thermal protection testing at AC125V/15A
- Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) for some markets
- FCC compliance for electronic components
220V Certification Requirements:
- CE marking under Low Voltage Directive (LVD)
- IEC 60335-2-23 compliance for appliance safety
- Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) directive compliance
- RoHS compliance for material restrictions
- Various national certifications (CCC for China, PSE for Japan)
The testing complexity differs significantly:
- 110V models undergo water immersion and GFCI response testing
- 220V models require high-voltage breakdown testing and insulation verification
- Both systems need thermal testing, but at different electrical ratings
- EMC testing is more stringent for 220V models in many markets
| Certification Aspect | 110V Requirements | 220V Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Standard | UL 859/1727 | IEC 60335-2-23 |
| Voltage Testing | AC125V breakdown | AC2500V breakdown |
| Safety Focus | Water protection | Insulation integrity |
| EMC Requirements | Moderate | Extensive |
| Cost Impact | $3,000-8,000 | $5,000-15,000 |
Certification timing also varies, with 110V UL testing typically taking 6-8 weeks, while 220V CE marking can require 8-12 weeks depending on the scope of testing required.
How Do Global Market Preferences Influence Manufacturing Decisions?
Understanding regional preferences helps manufacturers optimize their product portfolios and production strategies. Market preferences extend beyond voltage requirements to include performance characteristics and feature expectations.
Global market analysis shows that 220V markets generally prefer higher wattage models (1800-2200W) with advanced features, while 110V markets often prioritize safety features and compact designs. These preferences influence manufacturing decisions beyond basic voltage requirements.
Regional market characteristics reveal distinct patterns:
North American Market (110V) Preferences:
- Emphasis on safety features and GFCI protection
- Preference for compact, lightweight designs
- Strong demand for ionic and tourmaline technologies
- Price sensitivity in mid-market segments
European Market (220V) Preferences:
- Higher wattage models (2000W+) for faster drying
- Premium materials and advanced technologies
- Energy efficiency consciousness
- Sophisticated heat and speed control systems
Asian Market (220V) Preferences:
- Compact designs suitable for smaller living spaces
- Advanced ionic technologies for hair protection
- Smart features and digital controls
- Value-oriented pricing with good performance
The manufacturing implications include:
- 220V models benefit from higher wattage capabilities
- 110V models require more sophisticated safety integration
- Feature expectations vary significantly by region
- Cost optimization strategies differ by target market
| Market Region | Preferred Wattage | Key Features | Price Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| North America | 1200-1875W | Safety, compact design | Medium |
| Europe | 1800-2200W | Performance, efficiency | Low |
| Asia-Pacific | 1600-2000W | Technology, value | High |
| Emerging Markets | 1400-1800W | Reliability, affordability | Very High |
These preferences help manufacturers prioritize R&D investments and production configurations for different market segments.
Summary
Manufacturing differences between 110V and 220V hair dryers encompass motor specifications, heating elements, circuit boards, safety features, and certification requirements. 110V models require motors designed for higher current draw (15-20 amps) with complex switching circuits, while 220V systems operate more efficiently at lower current (8-10 amps) but need enhanced insulation. Cost differences range from 15-25% between voltage types, with 220V models generally more cost-effective for global distribution covering 70-75% of world markets.
Ready to optimize your global hair dryer sourcing strategy? Our Conason P1C high-speed hair dryer is available in both 110V and 220V configurations, engineered to meet the specific requirements of your target markets. Explore our complete product collection featuring voltage-optimized designs for global distribution, or contact our technical team for detailed specifications and wholesale pricing tailored to your regional requirements.